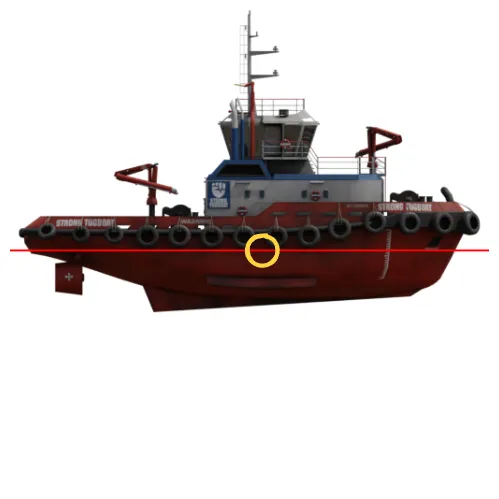
Bifrost metadata¶
When downloading a collection, a COCO JSON file is included in the ZIP archive. In addition to the standard COCO fields, the file would also contain metadata specific to Bifrost renders.
This custom metadata is located under the images and annotations sections of the JSON, within a field named bifrost_metadata.
Example format
{
"images": [
{
"id": 1,
"file_name": "e8c419d6-e9d8-49e0-ad43-161aadc4b9c9/RGB_camera_0.jpg",
"bifrost_metadata": {
"bifrost_camera_position": {
"x": 0,
"y": 0,
"z": 1000
},
"bifrost_camera_rotation": {
"roll": 0,
"pitch": -30,
"yaw": 0
},
"bifrost_camera_heading": 0.0,
"bifrost_camera_fov": 90.0
}
}
],
"annotations": [
{
"id": 1,
"image_id": 1,
"bifrost_metadata": {
"bifrost_object_id": "boat_1",
"bifrost_heading_absolute_degrees": 90.02760314941406,
"bifrost_distance_to_camera_m": 34.114948730468754,
"bifrost_absolute_position_m": {
"x": 32.7561962890625,
"y": 0.5690269851684571,
"z": 0.4848830032348633
},
"bifrost_absolute_rotation_degrees": {
"roll": -0.8629000186920166,
"pitch": 90.02760314941406,
"yaw": -1.8286000490188599
},
"bifrost_absolute_centroid_position_m": {
"x": 33.5,
"y": 1.2,
"z": 5.8
},
"bifrost_absolute_size_m": {
"x": 20.299549560546875,
"y": 21.7643212890625,
"z": 65.81230957031251
},
"bifrost_absolute_cuboid_positions_m": [
{"x": 23.15, "y": -9.68, "z": -27.12},
{"x": 43.85, "y": -9.68, "z": -27.12},
{"x": 23.15, "y": 12.08, "z": -27.12},
{"x": 43.85, "y": 12.08, "z": -27.12},
{"x": 23.15, "y": -9.68, "z": 38.69},
{"x": 43.85, "y": -9.68, "z": 38.69},
{"x": 23.15, "y": 12.08, "z": 38.69},
{"x": 43.85, "y": 12.08, "z": 38.69}
],
"bifrost_scale": {
"x": 1,
"y": 1,
"z": 1
}
}
}
]
}
Image level metadata¶
By default, the following information is exported under the images.bifrost_metadata field:
Field Name |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Meters |
Camera position in Bifrost world coordinates. |
|
Degrees |
Camera rotation relative to Bifrost world. |
|
Degrees |
Camera heading relative to Bifrost world. |
|
Degrees |
Horizontal field of view of the camera. |
Object level metadata¶
Note
Object level metadata is only available for assets added to the World via
world.add.
Objects such as Sky, Land, and Water would not have any associated metadata.
By default, the following information is exported under the annotations.bifrost_metadata field:
*If you require a different method of distance calculation, please let us know!
Adding custom metadata¶
Note
Custom metadata can currently only be added at the image level.
Annotation-level custom metadata is not supported at this time.
Add custom metadata for each frame using
scenario.set_metadata_keyframe.
scenario.set_metadata_keyframe(<frame_index>, <key>, <value>)
An important behavior to note is that metadata keys set in a previous frame will automatically persist
into subsequent frames unless explicitly updated. To remove a key from a specific frame, set its value
to METADATA_UNSET_KEY.
Here is a full example of how to add custom metadata
from bbi import *
world = World(...)
scenario = world.new_scenario(3)
# Frame 0
scenario.set_metadata_keyframe(0, "weather", "rainy")
scenario.set_metadata_keyframe(0, "sun", {"elevation": 30, "azimuth": 180})
scenario.set_metadata_keyframe(0, "special_key", 1)
# Frame 1
scenario.set_metadata_keyframe(1, "weather", "sunny")
scenario.set_metadata_keyframe(1, "special_key", METADATA_UNSET_KEY)
# Frame 2
scenario.set_metadata_keyframe(2, "weather", "cloudy")
scenario.render()
Example output
{
"images": [
{
"id": 1,
"file_name": "e8c419d6-e9d8-49e0-ad43-161aadc4b9c9/RGB_camera_0.jpg",
"bifrost_metadata": {
"weather": "rainy",
"sun": {
"elevation": 30,
"azimuth": 180
},
"special_key": 1,
}
},
{
"id": 2,
"file_name": "e8c419d6-e9d8-49e0-ad43-161aadc4b9c9/RGB_camera_1.jpg",
"bifrost_metadata": {
"weather": "sunny",
"sun": {
"elevation": 30,
"azimuth": 180
},
}
},
{
"id": 3,
"file_name": "e8c419d6-e9d8-49e0-ad43-161aadc4b9c9/RGB_camera_2.jpg",
"bifrost_metadata": {
"weather": "cloudy",
"sun": {
"elevation": 30,
"azimuth": 180
},
}
}
],
}